

These measures are not effective and may result in injury. You should not apply kerosene, petroleum jelly, nail polish, or a hot match tip to remove the tick.
DOG TICK VS DEER TICK SKIN
Use a pair of fine point tweezers to grip the tick as close to the skin as possible and pull straight out with steady pressure.
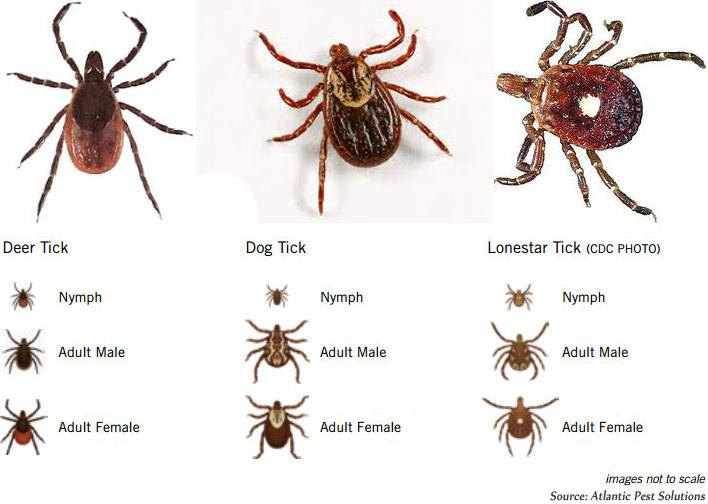
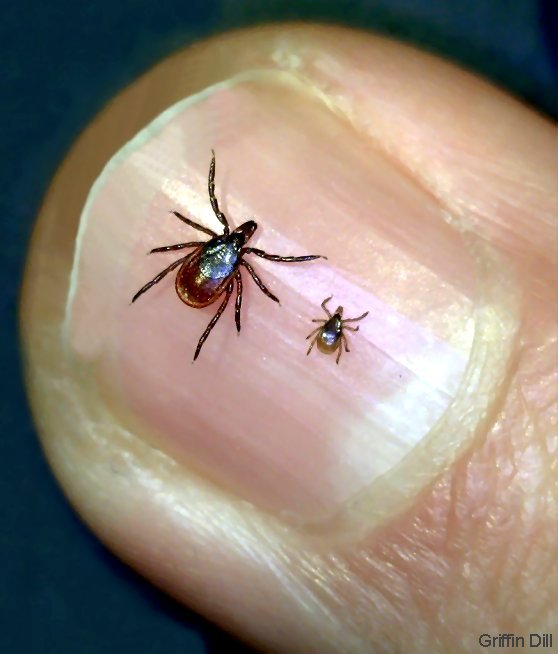
If you find a tick attached to your skin, don't panic. Ticks are tiny, so look for new "freckles". Check yourself, your children and your pets for ticks after coming inside:. Remove any attached ticks as soon as possible. Remember to check your children and pets, too. Favorite places ticks like to go on your body include areas between the toes, back of the knees, groin, armpits, and neck, along the hairline, and behind the ears. One of the most important things you can do is check yourself for ticks once a day. The nymph and adult females most frequently bite humans. Exposure to Lone Star tick saliva has been shown to cause an allergy to red meat in some people. Lone star tick saliva can be irritating but redness and discomfort at a bite site does not necessarily indicate any infection. Lone star ticks are not a significant source of human illness in Massachusetts at this time but are capable of spreading tularemia, ehrlichiosis and southern tick-associated rash illness (STARI). Adult dog ticks are about the size of a watermelon seed. The highest risk of being bitten by a dog tick occurs during the spring and summer seasons. In general, only the adult dog tick will bite humans. Dog Ticksĭog ticks are responsible for spreading Rocky Mountain spotted fever and certain types of tularemia. Black-legged tick nymphs are the size of a poppy seed and adults are the size of a sesame seed. However, adults can also be out searching for a host any time winter temperatures are above freezing. 
The highest risk of being bitten by this kind of tick occurs throughout the spring, summer and fall seasons. Both nymph (young) and adult black-legged ticks will bite humans. Black-legged Ticksīlack-legged ticks, sometimes called deer ticks, are responsible for spreading Lyme disease, babesiosis, anaplasmosis, Borrelia miyamotoi, and Powassan virus. Deer ticks and dog ticks are found throughout Massachusetts Lone Star ticks are also found in some places in Massachusetts. They attach to animals or people that come into direct contact with them. In Massachusetts, certain kinds of ticks can bite you and spread diseases like Lyme disease, babesiosis, anaplasmosis, tularemia, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Borrelia miyamotoi, and Powassan virus. Ticks are tiny bugs most likely found in shady, damp, brushy, wooded, or grassy areas (especially in tall grass), including your own backyard.ĭifferent kinds of ticks feed on the blood of mammals (including people, dogs, cats, deer, and mice), birds, or reptiles (snakes and turtles, for example).







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
